Luke 13 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Luke 13 is the thirteenth chapter of the
 This parable of Jesus (not to be confused with the
This parable of Jesus (not to be confused with the
Parables of Jesus: In the Light of Its Historical, Geographical & Socio-Cultural Setting
', Tate Publishing, 2008, , pp. 235-237. Fig trees were often planted in vineyards.Peter Rhea Jones,
Studying the Parables of Jesus
', Smyth & Helwys, 1999, , pp. 123-133. The fig tree was a common symbol for Israel, and may also have that meaning here, or the tree in the parable may refer to the religious leadership. In either case, the parable reflects Jesus offering his hearers one last chance for repentance. "These three years" logically refers to the period of Jesus' ministry. The parable has been connected to the miracle of cursing the fig tree. Richard Whately commented that this parable "is one which our Lord may be said to have put before his hearers twice; once in words, once in action." Richard Whately,
Lectures on Some of the Scripture Parables
', John W. Parker and Son, 1859, p. 153. Although the parable is found only in Luke's gospel, critics consider that there is no strong argument against its authenticity, for example a majority of the members of the Jesus Seminar voted it authentic.
 This healing miracle of Jesus appears only in the
This healing miracle of Jesus appears only in the

 This parable is one of the shorter
This parable is one of the shorter
Lamb translation
an
The plant referred to here is generally considered to be
The Gospel of Luke: A commentary on the Greek text
', Eerdmans, 1978, , pp. 561. but growing from a proverbially small seed: this smallness is also used to refer to faith in Matthew 17:20 and Luke 17:6. According to rabbinical sources, Jews did not grow the plant in gardens, and this is consistent with Matthew's description of it growing in a field. Luke tells the parable with the plant in a garden instead; this is presumably recasting the story for an audience outside Palestine.
 The parable of the leaven (also called the ''parable of the yeast'') is one of the shorter
The parable of the leaven (also called the ''parable of the yeast'') is one of the shorter
Greek Testament Critical Exegetical Commentary - Alford
on Luke 13, accessed 14 January 2022 although the answer, that the gate is narrow, and "many, I say to you, will seek to enter and will not be able", is also recorded in Matthew 7:13.
English Translation with Parallel Latin Vulgate''Online Bible'' at GospelHall.org
(ESV, KJV, Darby, American Standard Version, Bible in Basic English)
Multiple bible versions at ''Bible Gateway''
(NKJV, NIV, NRSV etc.) {{Gospel of Luke Gospel of Luke chapters
Gospel of Luke
The Gospel of Luke), or simply Luke (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). tells of the origins, birth, ministry, death, resurrection, and ascension of Jesus Christ. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-vol ...
in the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chri ...
of the Christian Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
. It records several parables
A parable is a succinct, didactic story, in prose or verse, that illustrates one or more instructive lessons or principles. It differs from a fable in that fables employ animals, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature as characters, ...
and teachings told by Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
and his lamentation over the city of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
.Halley, Henry H.,''Halley's Bible Handbook'': an Abbreviated Bible Commentary. 23rd edition. Zondervan Publishing House. 1962. Jesus resumes the journey to Jerusalem which he had embarked upon in Luke 9:51. The author of this chapter is unattributed, however early Christian tradition generally accepts that Luke the Evangelist composed this Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
as well as the Acts of the Apostles.Holman Illustrated Bible Handbook. Holman Bible Publishers, Nashville, Tennessee. 2012.
Text
The original text was written inKoine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
. This chapter is divided into 35 verses.
Textual witnesses
Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter are: * Papyrus 75 (AD 175-225) * Papyrus 45 (~250) *Papyrus 138 (3rd century; extant verses 13–17, 25–30) *Codex Vaticanus
The Codex Vaticanus ( The Vatican, Bibl. Vat., Vat. gr. 1209), designated by siglum B or 03 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), δ 1 ( von Soden), is a fourth-century Christian manuscript of a Greek Bible, containing the majority of the Greek Old ...
(325-350)
*Codex Sinaiticus
The Codex Sinaiticus ( Shelfmark: London, British Library, Add MS 43725), designated by siglum [Aleph] or 01 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 2 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscript ...
(330-360)
*Codex Bezae
The Codex Bezae Cantabrigiensis, designated by siglum D or 05 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 5 (in the von Soden of New Testament manuscript), is a codex of the New Testament dating from the 5th century writ ...
(~ 400)
*Codex Washingtonianus
The Codex Washingtonianus or Codex Washingtonensis, designated by W or 032 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), ε 014 ( Soden), also called the ''Washington Manuscript of the Gospels'', and ''The Freer Gospel'', contains the four biblical gospels an ...
(~ 400)
*Codex Alexandrinus
The Codex Alexandrinus (London, British Library, Royal MS 1. D. V-VIII), designated by the siglum A or 02 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 4 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscripts), is a manu ...
(400-440)
Sub-divisions
The New King James Version organises this chapter as follows (with cross references to other parts of the Bible): * = Repent or Perish * = The Parable of the Barren Fig Tree () * = A Spirit of Infirmity * = The Parable of the Mustard Seed (; ) * = The Parable of the Leaven () * = The Narrow Way * =Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
Laments over Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
(; see also )
Old Testament references
:Psalm
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived f ...
.
Repent or Perish (verses 1–5)
Jesus received a report thatPontius Pilate
Pontius Pilate (; grc-gre, Πόντιος Πιλᾶτος, ) was the fifth governor of the Roman province of Judaea, serving under Emperor Tiberius from 26/27 to 36/37 AD. He is best known for being the official who presided over the trial of ...
, who was described by Philo of Alexandria
Philo of Alexandria (; grc, Φίλων, Phílōn; he, יְדִידְיָה, Yəḏīḏyāh (Jedediah); ), also called Philo Judaeus, was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
Philo's de ...
as cruel, corrupt, and unnecessarily violent, had killed some Galileans while they were worshiping God by offering sacrifices according to the Jewish religious law. This discussion is only recorded in Luke's gospel, and the incident is not otherwise known to history.
Apparently those making the report, an identified group of people, were looking for Jesus to offer some explanation of why bad things happen to normal people, in this case even while they were worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity. It may involve one or more of activities such as veneration, adoration, praise, and praying. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recogniti ...
ing. They assume that a victim must have done something terrible for God to allow something so tragic to happen to them. Jesus denies that this is the case and answers that, likewise, the calamities suffered by the victims of the falling of the Tower of Siloam
The Tower of Siloam (, ''ho pyrgos en tō Silōam'') was a structure which fell upon 18 people, killing them. Siloam is a neighborhood south of Jerusalem's Old City. In the Gospel of Luke, Jesus refers to the tower's collapse and the death of ...
were not related to their relative sinfulness; he then diverts the focus onto the interrogators, wanting them to consider their own souls. ''Do you think that these Galileans were worse sinners than all the other Galileans, because they suffered in this way? No, I tell you; but unless you repent, you will all likewise perish.'' ''Or those eighteen on whom the tower in Siloam fell and killed them: do you think that they were worse offenders than all the others who lived in Jerusalem? No, I tell you; but unless you repent, you will all likewise perish.” ''His mention of the fall of the Tower of Siloam added a nuance to his prior point: accidents happen. Therefore, even in the absence of persecution, death can come unexpectedly to anyone, irrespective of how righteous or how sinful they are. He may have been emphasizing that the time granted by God for repentance is limited.
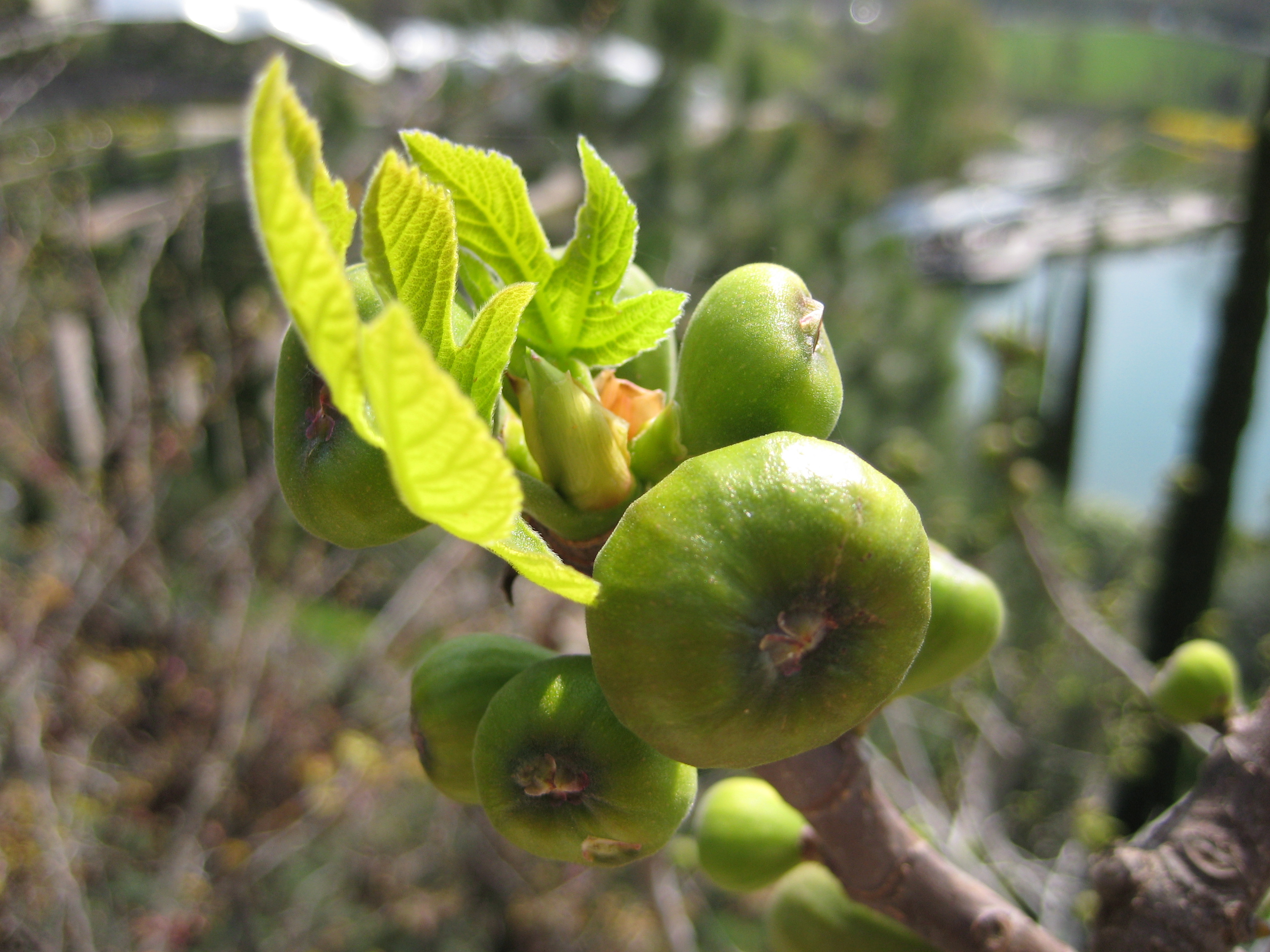
Parable of the barren fig tree (verses 6-9)

 This parable of Jesus (not to be confused with the
This parable of Jesus (not to be confused with the parable of the budding fig tree
A parable is a succinct, didactic story, in prose or verse, that illustrates one or more instructive lessons or principles. It differs from a fable in that fables employ animals, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature as characters, wh ...
) appears only in the Gospel of Luke
The Gospel of Luke), or simply Luke (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). tells of the origins, birth, ministry, death, resurrection, and ascension of Jesus Christ. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-vol ...
among the canonical gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
of the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chri ...
. In this parable, the owner is generally regarded as representing God, who had a fig tree ("tree of knowledge") planted in his vineyard ("the garden of Eden") and came seeking fruit ("righteous works", which in part is a mystery). The gardener (vinedresser) is God and the vine is Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
("tree of Life").Timothy Maurice Pianzin, Parables of Jesus: In the Light of Its Historical, Geographical & Socio-Cultural Setting
', Tate Publishing, 2008, , pp. 235-237. Fig trees were often planted in vineyards.Peter Rhea Jones,
Studying the Parables of Jesus
', Smyth & Helwys, 1999, , pp. 123-133. The fig tree was a common symbol for Israel, and may also have that meaning here, or the tree in the parable may refer to the religious leadership. In either case, the parable reflects Jesus offering his hearers one last chance for repentance. "These three years" logically refers to the period of Jesus' ministry. The parable has been connected to the miracle of cursing the fig tree. Richard Whately commented that this parable "is one which our Lord may be said to have put before his hearers twice; once in words, once in action." Richard Whately,
Lectures on Some of the Scripture Parables
', John W. Parker and Son, 1859, p. 153. Although the parable is found only in Luke's gospel, critics consider that there is no strong argument against its authenticity, for example a majority of the members of the Jesus Seminar voted it authentic.
Jesus healing a crippled woman on the Sabbath (verses 10–17)
 This healing miracle of Jesus appears only in the
This healing miracle of Jesus appears only in the Gospel of Luke
The Gospel of Luke), or simply Luke (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). tells of the origins, birth, ministry, death, resurrection, and ascension of Jesus Christ. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-vol ...
among the canonical gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
of the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chri ...
. According to Luke's account, Jesus was teaching in a synagogue on the Sabbath day, when he observed a woman who had been crippled "by a spirit" for eighteen years, and healed her with the words "You have been set free". This might therefore be classified as an exorcism
Exorcism () is the religious or spiritual practice of evicting demons, jinns, or other malevolent spiritual entities from a person, or an area, that is believed to be possessed. Depending on the spiritual beliefs of the exorcist, this may be ...
. The gospel account relates the story as another example of Jesus clashing with religious authorities over how the Sabbath should be honoured: when the synagogue ruler tells the woman she should have come to be healed on a different day, Jesus denounces the synagogue leaders as hypocrites because they would release their animals to feed on the Sabbath, so why should this "daughter of Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
" (verse 16) not be set free on the Sabbath from what is keeping her captive?
Verse 15 has the singular gr, υποκριτα, ''hypokrita'', in the Textus Receptus
''Textus Receptus'' (Latin: "received text") refers to all printed editions of the Greek New Testament from Erasmus's ''Novum Instrumentum omne'' (1516) to the 1633 Elzevir edition. It was the most commonly used text type for Protestant deno ...
, but the plural gr, υποκριταi, ''hypokritai'', in critical Greek texts such as the SBL Greek New Testament. Hence the King James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an Bible translations into English, English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and publis ...
reads "Thou hypocrite", addressing the synagogue leader only, whereas the New International Version reads "You hypocrites!". Free church minister William Robertson Nicoll
Sir William Robertson Nicoll (10 October 18514 May 1923) was a Scottish Free Church minister, journalist, editor, and man of letters.
Biography
Nicoll was born in Lumsden, Aberdeenshire, the son of Rev. Harry Nicoll (1812–1891), a Free Chu ...
suggests that the comment was "directed against the class", i.e. the synagogue leaders collectively.
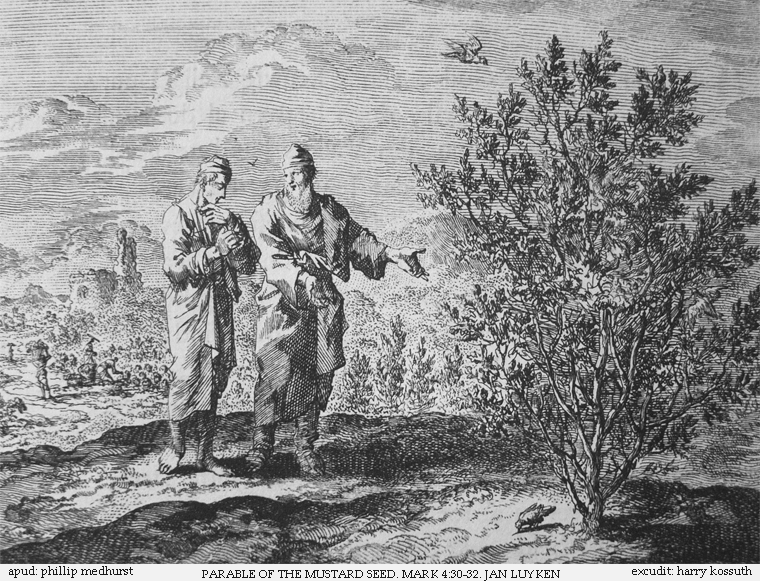
Parable of the Mustard Seed (verses 18-19)

 This parable is one of the shorter
This parable is one of the shorter parables of Jesus
The parables of Jesus are found in the Synoptic Gospels and some of the non-canonical gospels. They form approximately one third of his recorded teachings. Christians place great emphasis on these parables, which they generally regard as the wo ...
. It appears in three
3 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
3, three, or III may also refer to:
* AD 3, the third year of the AD era
* 3 BC, the third year before the AD era
* March, the third month
Books
* '' Three of Them'' (Russian: ', literally, "three"), a 1901 ...
of the canonical gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
of the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chri ...
. The differences between Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
s of Matthew (), Mark (), and Luke (), are minor. In the Gospels of Matthew and Luke, it is immediately followed by the Parable of the Leaven, which shares this parable's theme of the Kingdom of Heaven growing from small beginnings.
A version of the parable also occurs in the non-canonical Gospel of Thomas
The Gospel of Thomas (also known as the Coptic Gospel of Thomas) is an extra-canonical sayings gospel. It was discovered near Nag Hammadi, Egypt, in December 1945 among a group of books known as the Nag Hammadi library. Scholars speculate ...
20.''Gospel of Thomas''Lamb translation
an
The plant referred to here is generally considered to be
black mustard
''Brassica nigra'', or black mustard, is an annual plant cultivated for its dark-brown-to-black seeds, which are commonly used as a spice. It is native to tropical regions of North Africa, temperate regions of Europe, and parts of Asia.
Desc ...
, a large annual plant up to tall, I. Howard Marshall, The Gospel of Luke: A commentary on the Greek text
', Eerdmans, 1978, , pp. 561. but growing from a proverbially small seed: this smallness is also used to refer to faith in Matthew 17:20 and Luke 17:6. According to rabbinical sources, Jews did not grow the plant in gardens, and this is consistent with Matthew's description of it growing in a field. Luke tells the parable with the plant in a garden instead; this is presumably recasting the story for an audience outside Palestine.
Parable of the Leaven (verses 20-21)
 The parable of the leaven (also called the ''parable of the yeast'') is one of the shorter
The parable of the leaven (also called the ''parable of the yeast'') is one of the shorter parables of Jesus
The parables of Jesus are found in the Synoptic Gospels and some of the non-canonical gospels. They form approximately one third of his recorded teachings. Christians place great emphasis on these parables, which they generally regard as the wo ...
. It appears in two of the canonical gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
of the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chri ...
and a version of the parable also occurs in the non-canonical Gospel of Thomas
The Gospel of Thomas (also known as the Coptic Gospel of Thomas) is an extra-canonical sayings gospel. It was discovered near Nag Hammadi, Egypt, in December 1945 among a group of books known as the Nag Hammadi library. Scholars speculate ...
(96). The differences between Matthew () and Luke () are minor. In both places the story immediately follows the Parable of the Mustard Seed, which shares this parable's theme of the Kingdom of Heaven growing from small beginnings.
The narrow gate (verses 22-30)
:''And He went through the cities and villages, teaching, and journeying toward Jerusalem.'' Luke reminds his readers of Jesus' journey, which was last mentioned in , and "of the urgency it proclaims, and the response it demands". He is asked whether there are only a few who are (or will be) saved, a question "peculiar to Luke",Alford, H.Greek Testament Critical Exegetical Commentary - Alford
on Luke 13, accessed 14 January 2022 although the answer, that the gate is narrow, and "many, I say to you, will seek to enter and will not be able", is also recorded in Matthew 7:13.
Jesus laments over Jerusalem (verses 31-35)
Jesus confirms that he must continue to Jerusalem. Both here, on the journey, and at when the city is in sight, Jesus contemplates the significance and fate of Jerusalem, the holy city.See also
* Sermon on the Mount *Sermon on the Plain
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present contexts. ...
* Ministry of Jesus
* Parables of Jesus
The parables of Jesus are found in the Synoptic Gospels and some of the non-canonical gospels. They form approximately one third of his recorded teachings. Christians place great emphasis on these parables, which they generally regard as the wo ...
* Other related Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
parts: Psalm 6, Matthew 13
Matthew 13 is the thirteenth chapter in the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament section of the Christian Bible. Verses 3 to 52 of this chapter form the third of the five Discourses of Matthew, called the ''Parabolic Discourse'', based on th ...
, 23; Mark 4
Mark 4 is the fourth chapter of the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It tells the parable of the Sower, with its explanation, and the parable of the Mustard Seed. Both of these parables are paralleled in Matthew ...
; Luke 19
References
External links
* King James Bible - WikisourceEnglish Translation with Parallel Latin Vulgate
(ESV, KJV, Darby, American Standard Version, Bible in Basic English)
Multiple bible versions at ''Bible Gateway''
(NKJV, NIV, NRSV etc.) {{Gospel of Luke Gospel of Luke chapters